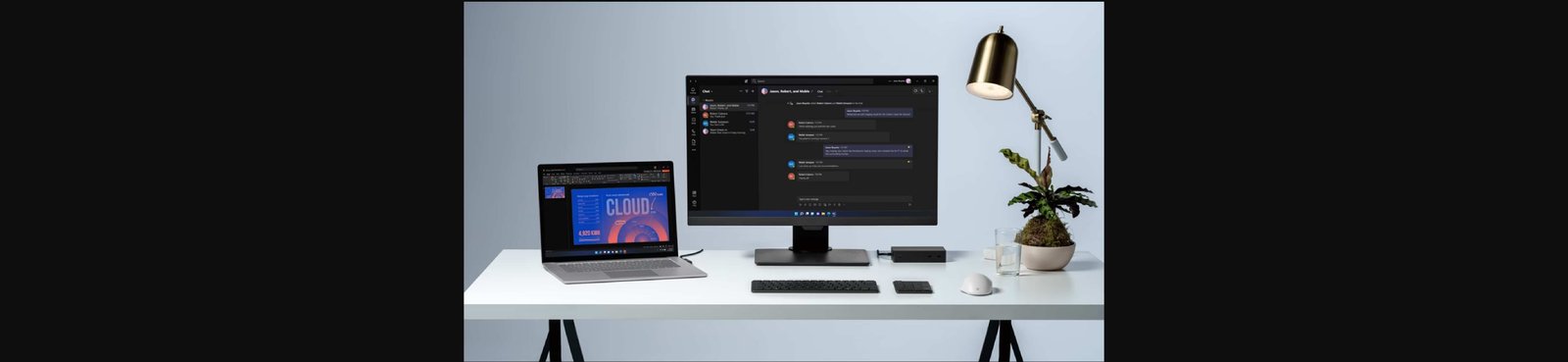
Before setting up dual monitors, ensure that your laptop supports multiple displays. Most modern laptops have either an HDMI, DisplayPort, or USB-C port for connecting external monitors. Some laptops may also support wireless connections to a second monitor using Wi-Fi.
What You Need to Check:
Video output ports: HDMI, DisplayPort, USB-C, or mini DisplayPort.
Graphics card capabilities: Ensure your laptop’s graphics card can support multiple monitors.
Laptop resolution: Verify that your laptop’s screen resolution supports the desired output on both screens.
To set up dual monitors, you’ll need the appropriate cables and adapters. For example:
HDMI to HDMI: If your laptop and monitor both support HDMI.
USB-C to HDMI/DisplayPort: If your laptop has a USB-C port and your monitor uses HDMI/DisplayPort.
VGA to HDMI/DisplayPort: If you are using older monitors.
Tip: Ensure the cable is long enough to comfortably reach your monitor from the laptop.
Start by connecting the first monitor to your laptop. This can typically be done using an HDMI cable, VGA, or DisplayPort depending on the ports available on your laptop and monitor. Ensure the monitor is powered on.
For dual monitors, connect the second monitor to your laptop using the appropriate cable and port. If your laptop only has one video output port, you may need a USB-to-HDMI adapter or a docking station that allows multiple connections.
Tip: If you’re using wireless connections (e.g., using Miracast), ensure that both your laptop and monitor support this feature.
Once the monitors are connected, the next step is configuring them in your laptop’s settings.
For Windows:
Right-click on your desktop and select Display settings.
Scroll down to Multiple displays.
Select the display arrangement (Extend, Duplicate, or Second screen only).
Drag the display icons to arrange them as they are physically placed on your desk.
For macOS:
Open System Preferences and select Displays.
Click on Arrangement to adjust the monitors.
Drag and drop the display icons to match the physical layout of your screens.
Once the monitors are connected, you can adjust the resolution and orientation for optimal viewing.
For Windows:
In Display settings, click on each monitor to adjust its resolution and orientation.
Ensure both monitors are set to their native resolution for the best image quality.
For macOS:
Under Display settings, select the Scaled option for each monitor to set the appropriate resolution.
Adjust the orientation if needed, especially if using a vertical display.
You can further customize your dual monitor setup, such as selecting the primary monitor (where your taskbar and icons will appear) and tweaking color settings. For a smooth experience, ensure that both monitors are set to a similar resolution.
Now that your dual monitors are set up, you can use them for increased productivity. You can use one screen for browsing, research, or communication apps and the other for your primary work. Apps like Microsoft Office, Google Docs, and design software work wonderfully in dual monitor setups.
Windows: Use Windows Key + P to quickly toggle between different display modes (Duplicate, Extend, Second screen only).
macOS: Use Mission Control to quickly switch between open apps and monitors.
If your dual monitors are not displaying correctly, try the following:
Check connections: Ensure all cables are securely connected.
Restart your laptop: Sometimes, a quick restart can resolve issues.
Update drivers: Ensure your laptop’s graphics drivers are up to date.
Check display settings: Verify that your display settings are correctly configured.
Setting up dual monitors on your laptop can enhance your work efficiency by providing more screen real estate. With the right cables, adapters, and display settings, you can seamlessly integrate dual monitors into your laptop setup. Whether you’re working from home, editing videos, or multitasking, dual monitors are a great way to boost productivity and improve your workflow.

Comments